STRATEGIC PREVENTION FRAMEWORK
SEQUENTIAL COMPONENTS
Assessment
The data and understanding gained can help the coalition show the community and its leaders the important relationship between anti-drug coalition work and the community’s stated priorities.
Capacity
This process may be different than the way some coalitions operate. Targeted recruitment and engagement means “getting the right person to the right meeting at the right time.”
Planning
A development of a logic model is crucial in the process to design and selected effective strategies for your community. We’ve outlined four key components, which make up good logic models.
Implementation
The effort to change the behaviors and conditions associated with each local condition on a logic model requires the implementation of 3 key strategies: Environmental, Evidence-based, and Comprehensive.
Evaluation
What makes coalition evaluation so important is the powerful things people can do with the results. This section outlines 5 uses or functions for information gathered through evaluation.
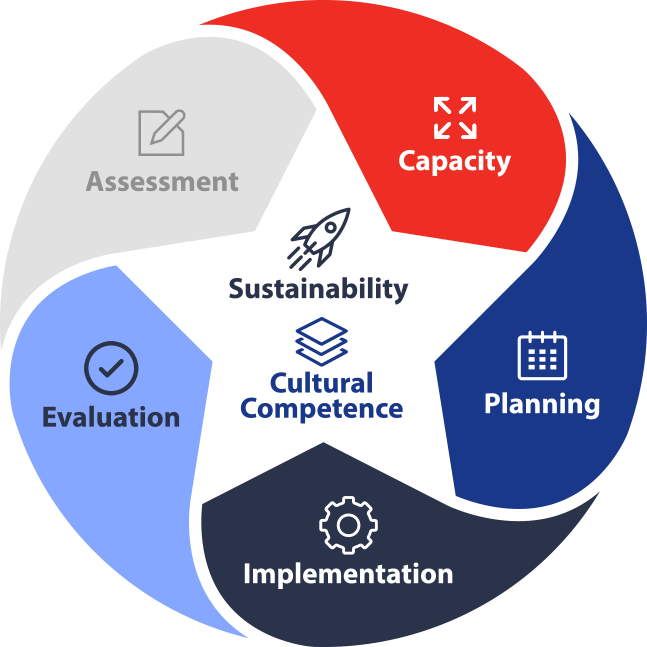
CROSS CUTTING COMPONENTS
Sustainability
There are 4 things coalitions must sustain — strong membership, a credible process, a connection to current community issues, and the resources needed to support daily work.
Cultural Competence
Cultural Competence affects all aspects of coalition building. Maintain a strong focus on your community and its needs, avoiding “borrowing” another groups cultural competence plan and using it as your own.


